Here we can see, “How to Disable “Reserved Storage” on Windows 10”
What is Reserved Storage?
Windows updates necessitate a certain amount of free disc space. If your PC does not have enough free space, updates will not install. Microsoft aims to fix this problem with the May 2019 Update by reserving disc space for future updates.
Previously, if your PC didn’t have enough free disc space, Windows would fail to install updates properly. The only way to get around this is to clear some storage space before proceeding.
Microsoft requires Windows 10 to set aside at least 7 gigabytes of space on your hard drive for updates to download, regardless of how much disc space you have.
Reserved Storage will be used for apps, temporary files, and system caches when not being used by updating files, improving the day-to-day functionality of your PC.
In other words, reserved storage doesn’t necessarily imply that Windows is using the entire additional 7 GB of space—more it’s likely that it’s storing temporary files that would otherwise be stored elsewhere on your system drive.
How to Check If Your PC Has Reserved Storage
Before you go any further, double-check that your System is configured to use Reserved Storage. There’s no need to continue if it doesn’t because Windows isn’t setting aside any extra space on your device.
The Settings app allows you to see if and how the System is using much extra storage.
This feature will be enabled by default on new PCs that come pre-installed with Windows 10 version 1903 (the May 2019 Update), as well as clean installs of Windows 10 version 1903. Reserved Storage will not be enabled if you upgrade from a previous version of Windows 10.
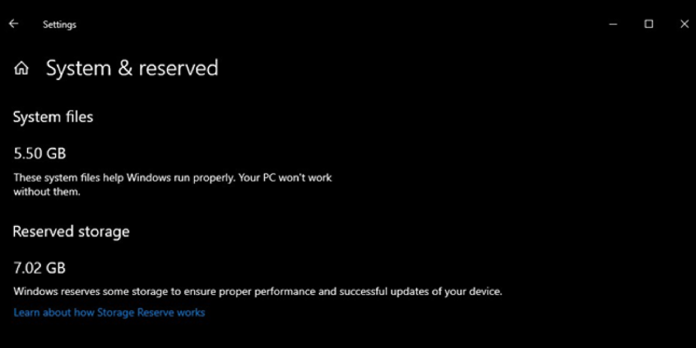
- Go to Settings > System > Storage to see if Windows is using Reserved Storage. (To open the Settings app quickly, press Windows+i on your keyboard.) Then, under the list of items taking up space, click “Show More Categories.”
- Select “System & Reserved” from the drop-down menu.
- If you have reserved storage enabled on your PC, you will see a section called “Reserved Storage” with 7+ GB of storage space in use. If you don’t see “Reserved Storage” here, the “Storage Reserve” feature isn’t enabled on your System.
Should Reserved Storage Be Disabled?
Optional features (Settings > Apps & Features > Manage Optional Features) and language packs (Settings > Time & Language > Language) can be uninstalled to free up some reserved storage space.
However, if you want to free up the most space possible, you’ll need to entirely turn off the reserved storage feature. Microsoft advises against this, stating:
Our goal is to improve your PC’s day-to-day performance by ensuring that critical OS functions have constant access to disc space. If a user’s storage is nearly complete and there is no reserved storage, several Windows and application scenarios become unreliable. If Windows and applications require free space to function, they may not perform as expected. Updates, apps, temporary files, and caches are less likely to consume valuable free space and should continue to function as expected with reserved storage.
However, if you require more space, you may continue and disable reserved storage. After all, most Windows 10 PCs have this turned off and are functioning normally in the real world.
How to Disable Reserved Storage
Before you go any further, keep in mind the following: Your change will not take effect right away. We tested this and found that the reserved storage will not be removed from your System until the next time Windows updates. Thankfully, after we made the below change, a simple cumulative update—the kind Microsoft releases every month—removed the reserved storage. (This may change in the future; Microsoft does not want this removed.)
Now that we’ve gotten that out of the way, let’s look at using the Registry Editor to disable Reserved Storage.
Standard Caution: The Registry Editor is a powerful tool, and misusing it can make your System unstable, if not completely unusable. This is a reasonably straightforward hack, and as long as you follow the instructions, you should be fine. If you’ve never used the Registry Editor before, you should read up on how to use it before getting started. Before making any changes, make sure you back up the Registry (and your computer!).
- By pressing Start and typing “regedit,” you can access the Registry Editor. To open the Registry Editor, press Enter and allow it to make changes to your computer.
- Use the left sidebar of the Registry Editor to navigate to the following key. You can also copy and paste it into the address bar of the Registry Editor.
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\ReserveManager
- Double-click on ShippedWithReserves once you’ve arrived.
- Click “OK” after changing the number under “Value Data” from 1 to 0.
That is all there is to it. Close Registry Editor and restart Windows to see the changes take effect.
Your change has been applied, but it may take a few weeks for Windows to install an update and delete the reserved storage.
Conclusion
I hope you found this information helpful. Please fill out the form below if you have any questions or comments.
User Questions:
- What is Windows 10’s reserved storage?
Windows reserves a portion of your device’s storage space for temporary files, caches, and other files to ensure that it can successfully update and run at its best. When your device runs out of reach, Windows will free up reserved storage so that it can be used for other tasks, such as installing a Windows update.
- Can I delete Windows 10’s reserved storage?
Go to Settings > Apps > Apps & features > Manage optional features to see which parts are installed on your device. By uninstalling optional features that you do not use, you can reduce the amount of space required for reserved storage on your device.
- Is it possible to delete the reserved partition?
However, you can’t simply delete the System Reserved partition. If you delete this partition, Windows will not boot appropriately because the boot loader files are stored there. Therefore, before you can delete the System Reserved partition, you must first copy the boot files to the main Windows system drive.
- How can I reduce the amount of System and reserved storage used for updates?
How to reduce system and reserved storage for update? from windows
- Ridiculously High Storage Used Up for [System & reserved]
Ridiculously High Storage Used Up for [System & reserved] from Windows10