Here we can seee, “How to Test Your Network Using the Ping Command”
The ping command transmits data packets to a certain IP address on a network and then tells you how long it took to send and receive that data. It’s a useful tool for quickly testing different parts of your network. Here’s how to put it to good use.
What precisely is ping?
A ping command can be sent from a Windows, Mac, or Linux computer. It’s a useful programme that dates back to the early 1980s. The phrase is derived from sonar technology, which puts out a sound wave and then listens for pings (or echoes) in response. The longer the spacing, the further an object must be from the observer.
As data requests travel throughout the world, the same logic applies to networks. Pinging can also alert you to network congestion or other latency issues, such as a down server. The process of performing a ping test is quite simple.
What Is Ping and How Does It Work?
Ping is a phrase used in sonar technology that sends sound pulses and then listens for the return echo. On a computer network, most operating systems provide a ping utility that functions similarly. The ping command is used in conjunction with a specified URL or IP address. Your computer sends a series of data packets to that device and then waits for a response. When it receives a response, the ping tool displays the time it took each packet to complete the round trip—or informs you that no answer was received.
It appears to be straightforward, and it is. However, you may make good use of it. For example, you may see if your computer can connect to another device on your local network, such as your router, or if it can connect to a device on the Internet. This might assist you in determining whether a network problem is occurring on your local network or elsewhere. In addition, the amount of time it takes packets to return to you can help you diagnose a slow connection or packet loss.
It doesn’t matter what operating system you’re using, either. You may use ping on macOS, Linux, or any version of Windows by opening a terminal or Command Prompt window.
How to perform a network ping test
The instructions for doing a ping network test vary depending on the operating system.
In Windows 10, go to the taskbar and type:
- To open the Command Prompt, type “cmd.”
- Open a Command Prompt window.
- In the black box, type “ping” and press the space bar.
- Ping the IP address that you want to ping (e.g., 192.XXX.X.X).
- Examine the ping results that have been displayed.
On a Mac, repeat the process by launching Network Utility and entering the hostname or IP address to ping.
Open Terminal if you’re using Linux. You can also use the traceroute command to examine the many IP addresses through which your request travels. To do so, follow these steps:
- Open the Terminal application.
- To trace an IP address or URL, type “traceroute” followed by the address or URL you want to trace.
- Press Enter to see the results.
What are some typical ping addresses?
When running ping testing, you can start by checking your internet connectivity. To do so, double-check that the IP address you’re pinging is up and running.
While any address may experience downtime at some point, the following are some reliable options for you to ping:
- 208.67.222.222 and 208.67.220.220 (OpenDNS)
- 1.1.1.1 and 1.0.0.1 (Cloudflare)
- 8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4 (Google DNS)
If you don’t get a response when you ping these IP addresses for connectivity, it’s most likely because there’s an issue on your end.
Ping Command Syntax
ping [-t] [-a] [-n count] [-l size] [-f] [-i TTL] [-v TOS] [-r count] [-s count] [-w timeout] [-R] [-S srcaddr] [-p] [-4] [-6] target [/?]
| Ping Command Options | |
|---|---|
| Item | Explanation |
| -t | This option will ping the target until Ctrl+C stops it. |
| -a | This ping command option resolves a target’s hostname if possible. |
| -n count | The number of ICMP Echo Requests sent can be configured from 1 to 4294967295. If -n isn’t used, ping sends 4 by default. |
| -l size | Set the size of the echo-request packet in bytes from 32 to 65,527. If you don’t use the -l option, ping sends a 32-byte echo request. |
| -f | Use this ping command option to prevent routers from fragmenting ICMP Echo Requests. The -f option is commonly used for debugging PMTU difficulties. |
| -i TTL | This option sets the Time to Live (TTL) value, the maximum of which is 255. |
| -v TOS | This option lets you specify the TOS. Unfortunately, this feature is no longer functional in Windows 7 but remains for compatibility. |
| -r count | Use this ping command option to record and display the number of hops between your computer and the target computer or device. If you want to see all the hops between two devices, use the tracert command instead. |
| -s count | Use this option to report the time of each echo request and reply in Internet Timestamp format. For example, with a count of 4, just the first four hops can be timestamped. |
| -w timeout | Specifying a timeout value while running ping modifies the amount of time it waits for each reply. If the -w option is not provided, the default timeout value of 4000 is utilized. |
| -R | This parameter instructs ping to track the return path. |
| -S srcaddr | Specify the source address here. |
| -p | The Hyper-V Network Virtualization provider address is pingable. |
| -4 | This forces the ping command to utilize IPv4 exclusively, but only if the target is a hostname. |
| -6 | This, like the -4 option, is only required when pinging a hostname. |
| target | This is the target, either an IP address or a hostname. |
| /? | You can use the ping help switch to get more information about the command’s options. |
So, what are your options for Ping?
Here are some cool things you can do with the command now that you know how to use it:
- To see if you can access an internet destination, ping a URL (www.ITechbrand.com) or an IP address. If you receive a successful response, you can assume that all networking equipment between you and the destination are operational, including your computer’s network adapter, your router, and any internet devices between your router and the destination. If you want to dig deeper into those paths, you can use tracert, another networking tool.
- Ping a URL to find out what its IP address is. You can use the ping command to find out the IP address of a URL. The IP address that the ping tool is using is displayed right at the top.
- Check to see if you can reach your router by pinging it. If you’re having trouble pinging an internet location, try pinging your router. A successful response indicates that your local network is operational and that the problem connecting to the Internet is outside your control.
- Your loopback address should be pingable (127.0.0.1). If you can’t ping your router, but it appears to be turned on and functioning, try pinging a loopback address. The address is always 127.0.0.1, and pinging it successfully indicates that your computer’s network adapter (and the networking software in your OS) are both operational.
Note: Other machines on your local network may not respond to ping requests because their built-in firewalls restrict them from responding to ping requests. You’ll need to disable that setting to enable pings through the firewall if you wish to ping those devices.
The list above employs an outside-in method, in which the farthest target is pinged first, followed by the more proximate devices. For example, some users choose to ping the loopback address first, followed by their router (or another local device), and finally, an internet address.
Examples of Ping Commands
Several commands that use ping are listed below.
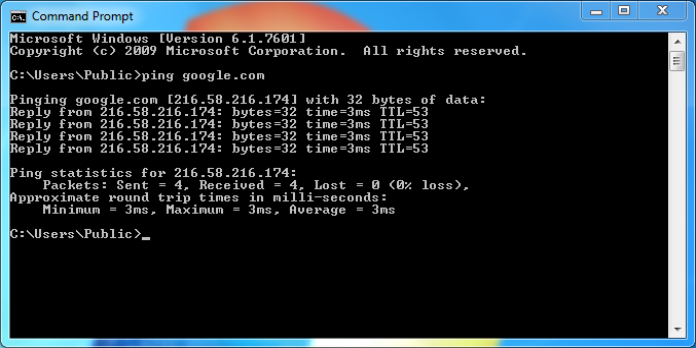
Ping Google.com
ping -n 5 -l 1500 www.google.comThe ping command is used to ping the hostname www.google.com in this example. The -n option instructs the ping command to transmit 5 ICMP Echo Requests instead of the default of 4, and the -l option increases the packet size for each request to 1500 bytes from 32 bytes.
The following is an example of what the Command Prompt window will show:
Reply from 172.217.1.142: bytes=1500 time=30ms TTL=54Reply from 172.217.1.142: bytes=1500 time=30ms TTL=54Reply from 172.217.1.142: bytes=1500 time=29ms TTL=54Reply from 172.217.1.142: bytes=1500 time=30ms TTL=54Reply from 172.217.1.142: bytes=1500 time=31ms TTL=54Ping statistics for 172.217.1.142:Packets: Sent = 5, Received = 5, Lost = 0 (0% loss),Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:Minimum = 29ms, Maximum = 31ms, Average = 30ms
Each ICMP Echo Request message sent to www.google.com was returned, as indicated by the 0 percent loss displayed under Ping statistics for 74.217.1.142. This means that it is perfectly capable of communicating with Google’s website as far as this network connection is concerned.
Ping localhost
ping 127.0.0.1Using this IP with the ping command is a great method to see if Windows’ network functions are working, but it tells nothing about your network hardware or connection to other computers or devices. ping::1 is the IPv6 version of this test.
Find Hostname With Ping
ping -a 192.168.1.22In this example, we’re using the ping command to find the hostname associated with the 192.168.1.22 IP address, but otherwise pinging it as usual.
For example, the command might resolve the IP address 192.168.1.22 as the hostname J3RTY22 and then run the rest of the ping with default settings.
Ping Router Command
ping 192.168.2.1This comma like the ping command samples above, is used to see if your computer can communicate with your router. The only difference is that we’re verifying the connection between the machine and the router instead of using a ping command switch or pinging the localhost (192.168.2.1 in this case).
If you’re having difficulties logging in to your router or accessing the Internet at all, use this ping command to see if it’s reachable, changing 192.168.2.1 with your router’s IP address, of course.
Ping With IPv6
ping -t -6 SERVERIn this example, we use the -6 argument to compel the ping command to utilise IPv6 and the -t option to ping SERVER forever. Ctrl+C can be used to manually stop the ping.
Conclusion
I hope you found this information helpful. Please fill out the form below if you have any queries or comments.
User Questions:
1. How can the ping command help in testing?
Ping is a command-line application that checks if a networked device is reachable and is available on practically any operating system with network connectivity. The ping command delivers a request to a specific device via the network.
2. What is the purpose of ping in networking?
Ping sends an Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) Echo Request to a specific network interface and waits for a response. A ping signal is sent to a specific address when a ping command is given. The destination host reacts by delivering an echo reply packet when it receives the echo request.
3. What is the result of my IP ping test?
It would help if you typed “ping 192.168.1.1” and hit Enter to ping it. Your computer will send a test data packet to the desired host and wait to respond once you start the ping. The computer will send four pings to validate that the test is meaningful.
4. A method for checking your ping without entering the game.
How to check your ping without getting into the game. from leagueoflegends
5. I’m using ping -t in prompt to monitor a server that I just remotely rebooted, and I’m getting responses, but the server isn’t back up?
Using ping -t in command prompt to monitor a server I just rebooted remotely, getting replies from ping command but server isn’t back up? from sysadmin